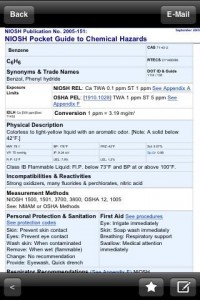
 Dangerous Decisions LLC today is proud to introduce the NIOSH Pocket Guide 1.0, their new chemical hazards database for iPhone and iPod touch. Designed specifically to take advantage of the iPhone’s interface, the NIOSH Pocket Guide (National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health) gives safety professionals immediate access to crucial information on all of 677 chemicals in the database including all the resources of the NIOSH Pocket Guide and much more.
Dangerous Decisions LLC today is proud to introduce the NIOSH Pocket Guide 1.0, their new chemical hazards database for iPhone and iPod touch. Designed specifically to take advantage of the iPhone’s interface, the NIOSH Pocket Guide (National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health) gives safety professionals immediate access to crucial information on all of 677 chemicals in the database including all the resources of the NIOSH Pocket Guide and much more.
The NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards (NPG) is intended as a source of general industrial hygiene information on several hundred chemicals (with their classes) for workers, employers, and occupational health professionals. It is a must-have for every safety professional, industrial hygienist, chemist, or collage student seeking a safety degree, and a valuable reference guide for anyone that works with hazardous chemicals in the workplace or at home.
The information found in the NIOSH Pocket Guide help users recognize and control occupational chemical hazards. The NPG does not contain an analysis of all pertinent data. Rather, it presents key information and data in abbreviated or tabular form for chemicals or substance groupings (e.g. cyanides, fluorides, manganese compounds) that are found in the work environment.
Designed as a stand-alone application, the Pocket Guide includes the chemical names, synonyms, trade names, conversion factors, CAS, RTECS, and DOT numbers, recommended exposure limits (NIOSH RELs), Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) Permissible Exposure Limits (PELs), and NIOSH Immediate Dangerous to Life and Health values (NIOSH IDLHs) (documentation for those values). The guide also features a physical description of the agent with chemical and physical properties, measurement methods, personal protection and sanitation recommendations, respirator recommendations, as well as great information on health hazards including route, symptoms, first aid and target organ information.
 Feature Highlights:
Feature Highlights:
* Chemical names, synonyms, trade names, conversion factors, CAS, RTECS, and DOT numbers
* NIOSH Recommended Exposure Limits (NIOSH RELs)
* Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) Permissible Exposure Limits (PELs)
* NIOSH Immediate Dangerous to Life and Health values (NIOSH IDLHs) (documentation for those values)
* A physical description of the agent with chemical and physical properties
* Measurement methods
* Personal protection and sanitation recommendations
* Respirator recommendations
* Information on health hazards including route, symptoms, first aid and target organ information
* Search by Chemical Name, Case number, Synonym and Trade Names
* Access all the appendixes
* Save critical information about regularly worked-with chemicals in the Notes section
* Use the convenient Email function to send Chemical guides and notes to associates
* Load onto all generations of iPhone and iPod Touch
* Download to iPhone devices without a wireless connection
“As a safety professional, when emergencies with hazardous chemicals occur, I was frustrated spending valuable time compiling critical response information from multiple sources to get the field a comprehensive safety plan” said Chester Karella, founder and CEO of Dangerous Decisions LLC. “There had to be a better way. My new NIOSH Pocket Guide App allows all the critical information to be quickly deployed to the field from a single application.”
System Requirements:
* iPhone or iPod Touch 3.0 or later
Pricing and Availability:
NIOSH Pocket Guide 1.0 is only $9.99 (USD) and available exclusively through the App Store in the Reference category. Free updates as Chemical exposures recommendations change will be made available. Review copies are available upon request.











 Dangerous Decisions LLC today is proud to introduce the NIOSH Pocket Guide 1.0, their new chemical hazards database for iPhone and iPod touch. Designed specifically to take advantage of the iPhone’s interface, the NIOSH Pocket Guide (National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health) gives safety professionals immediate access to crucial information on all of 677 chemicals in the database including all the resources of the NIOSH Pocket Guide and much more.
Dangerous Decisions LLC today is proud to introduce the NIOSH Pocket Guide 1.0, their new chemical hazards database for iPhone and iPod touch. Designed specifically to take advantage of the iPhone’s interface, the NIOSH Pocket Guide (National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health) gives safety professionals immediate access to crucial information on all of 677 chemicals in the database including all the resources of the NIOSH Pocket Guide and much more. Feature Highlights:
Feature Highlights: